|
ubaTaeCJ
a membrane bound structure that is the basic unit of life

a membrane bound structure that is the basic unit of life
what is a cell?


this person used a crude microscope to observe thin slices of cork cells.

this person used a crude microscope to observe thin slices of cork cells.

the first person to observe living cells.

the first person to observe living cells.
who is anton van leeuwenhoek?

the three parts of the cell theory.

the three parts of the cell theory.
what are
1. all living things are composed of one or more cells
2. cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism
3. cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells?

the three scientists who directly contributed evidence for the cell theory.
* as stated in our notes
* last names are valid

the three scientists who directly contributed evidence for the cell theory.
* as stated in our notes
* last names are valid
who are
1. matthias schleiden
2. theodor schwann
3. rudolph virchow?

alternative names for the cell membrane.
* 2 possible corect answers

alternative names for the cell membrane.
* 2 possible corect answers
what are lipid bilayer or fluid mosaic model?

the cell membrane is mostly made of these.

the cell membrane is mostly made of these.

the two parts of the phospholipid below and their characteristics.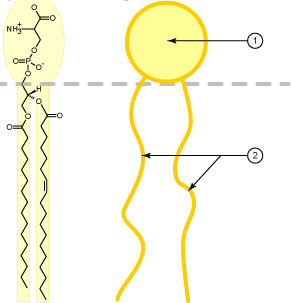

the two parts of the phospholipid below and their characteristics.
what are
1: polar head- hydrophilic
2: 2 non-polar tails- hydrophobic?

the type of protein that transmits signals and is located on either the exterior or interior surface.

the type of protein that transmits signals and is located on either the exterior or interior surface.
what is a peripheral/receptor protein?

act as sites where viruses or chemical messages can attach.

act as sites where viruses or chemical messages can attach.
what are carbohydrate chains?

the movement of like species from high concentration to low concentration.

the movement of like species from high concentration to low concentration.

type of solution when the concentration of dissolved substances outside the cell is same as the inside of the cell.

type of solution when the concentration of dissolved substances outside the cell is same as the inside of the cell.
what is isotonic?


a specialized membrane movement of k+, ca2+, cl-, and na+ ions.

a specialized membrane movement of k+, ca2+, cl-, and na+ ions.

the increase in pressure inside a cell while placed in an hypotonic solution.

the increase in pressure inside a cell while placed in an hypotonic solution.
what is turgor pressure?


the meaning of "hyper" in hypertonic.

the meaning of "hyper" in hypertonic.
what is "above strength"?

the form of energy required in active transport.

the form of energy required in active transport.
what is atp ( adenosine tri-phosphate)?

process by which cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles.

process by which cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles.
what is endocytosis?
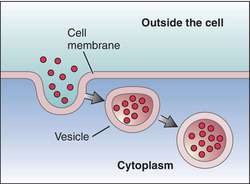

the process by which cells remove fluids, macromolecules, and large particles.

the process by which cells remove fluids, macromolecules, and large particles.
what is exocytosis?


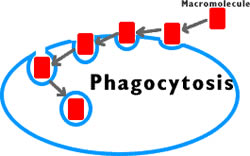
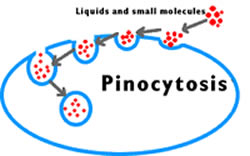
the two types of endocytosis and their differences.

the two types of endocytosis and their differences.
what are
pinocytosis- ingestion of water
phagocytosis- ingestion of particles (solids)?

the major difference between facilitated diffusion and na+/k+ pump.

the major difference between facilitated diffusion and na+/k+ pump.
what is na+/k+ pumps move substances against concentration gradient?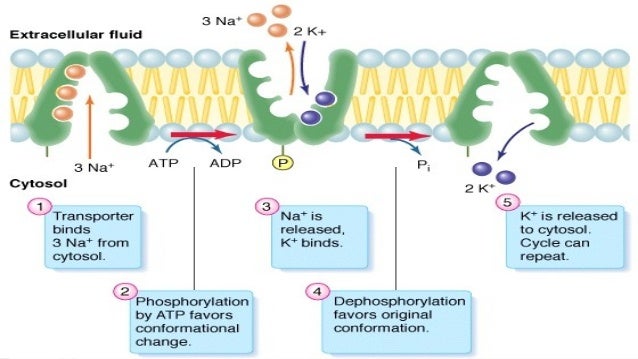

the type of solution best for plant cells.

the type of solution best for plant cells.
what is hypotonic?


phospholipid head faces ____ and tails face ____.

phospholipid head faces ____ and tails face ____.
what is 'outward' and 'inward'?


type of solution in which plasmolysis occurs.

type of solution in which plasmolysis occurs.
what is hypertonic?


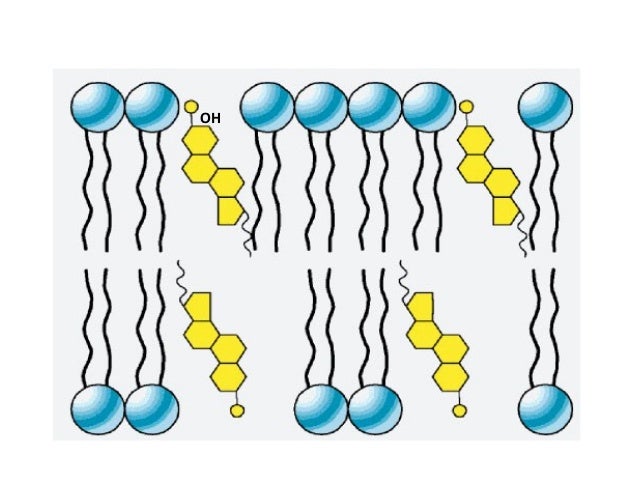
prevents fatty acid tails from sticking together.

prevents fatty acid tails from sticking together.
what is cholesterol?

the point in the process of diffusion when dynamic equilibrium is reached.

the point in the process of diffusion when dynamic equilibrium is reached.
what is when there is continuous movement but no change?
amount in= amount out


name all the parts of the cell membrane.
* all must be correct!!
* leave j out


name all the parts of the cell membrane.
* all must be correct!!
* leave j out
a: glycoprotein
b: glycolipid
c: carbohydrate (chain)
d: tails of phospholipid
e: phospholipids
f: heads of phospholipids
g: peripheral protein
h: cholesterol
i: integral proteins


| Team 1 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 2 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 3 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 4 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 5 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 6 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 7 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 8 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 9 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 10 |
 |
|
 |
|

What Would You Like To Risk?

| Team 1 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 2 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 3 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 4 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 5 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 6 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 7 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 8 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 9 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 10 |
 |
|
 |
|
Go To The Final Question
Final Score:

| Team 1 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 2 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 3 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 4 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 5 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 6 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 7 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 8 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 9 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 10 |
 |
|
 |
|

Edit This Game:

|
|




























