|
AP Chemistry Chapters 11, 12, 13
What is the energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid by a unit amount?

What is the energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid by a unit amount?

What are the attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule

What are the attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule

What is superconductivity?

What is superconductivity?
Frictionless flow of electrons through a substance.

The process by which solvent molecules surround and interact with solute ions or molecules is called...

The process by which solvent molecules surround and interact with solute ions or molecules is called...

What is the degree of randomess or disorder in a system given by a thermodynamic quantity?

What is the degree of randomess or disorder in a system given by a thermodynamic quantity?


Is this a Polar or a Non-Polar Bond?


Is this a Polar or a Non-Polar Bond?


What kind of bonding is present here.


What kind of bonding is present here.
Hydrogen bonding or London dispersion forces .

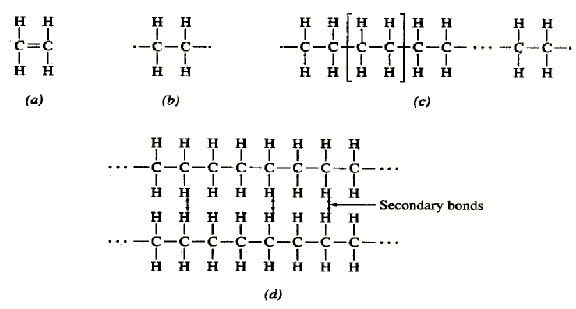 What are these structures representing? What are these structures representing?

 What are these structures representing? What are these structures representing?


What is this structure?


What is this structure?

Write a chemical equation that represents the formation of polychloroprene from chloroprene.

Write a chemical equation that represents the formation of polychloroprene from chloroprene.
CH2=CClCH=CH2 --> -[-CH2CCl=CHCH2-]-n

Write a chemical equation that represents the formation of polyacrylonitrile from acryonitrile1

Write a chemical equation that represents the formation of polyacrylonitrile from acryonitrile1
CH2=CHC*N --> -[-CH2CH(C*N)-]-n

Write a chemical equation for formation of a polymer via a condensation reaction from the monomers succinic acid (HOOCCH2CH2COOH) and ethylenediamine (H2NCH2CH2NH2)

Write a chemical equation for formation of a polymer via a condensation reaction from the monomers succinic acid (HOOCCH2CH2COOH) and ethylenediamine (H2NCH2CH2NH2)

Which member of the following pairs has the stronger intermolecular dispersion force:
Br2 or O2

Which member of the following pairs has the stronger intermolecular dispersion force:
Br2 or O2

Which member of the following pairs has the larger London dispersion forces:
H2O or H2S

Which member of the following pairs has the larger London dispersion forces:
H2O or H2S

What is the difference between a monomer and a polymer?

What is the difference between a monomer and a polymer?
A monomer is a single structure and has low moleculer weight, while a polymer consists of several monomers and appears like plastic such as shellac and varnish. A polymer has higher molecular weight.

List the three states of matter in order of increasing molecular disorder and increasing intermolecular attractions.

List the three states of matter in order of increasing molecular disorder and increasing intermolecular attractions.
The solid state has the least amount of disorder, the liquid state is intermediate between the solid and gaseous state, the gas state is the most disordered. The intermolecular forces are the strongest in the solid, intermediate in the liquid phase, and weakest in the gas phase.

For each of the follwing pairs of semiconductors, which one will have the larger band gap:
A) CdS or CdTe
B) GaN or InP
C) GaAs or InAs

For each of the follwing pairs of semiconductors, which one will have the larger band gap:
A) CdS or CdTe
B) GaN or InP
C) GaAs or InAs

Calculate the mass percentage of Na2SO4 in a solution containing 10.6 g Na2SO4 in 483 g water.

Calculate the mass percentage of Na2SO4 in a solution containing 10.6 g Na2SO4 in 483 g water.

Calculate the molarity of each of the follwing solutions:
A)8.66 g benzene (C6H6) dissolved in 23.6 g carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
B) 4.80 g NaCl dissolved in 0.350 L of water

Calculate the molarity of each of the follwing solutions:
A)8.66 g benzene (C6H6) dissolved in 23.6 g carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
B) 4.80 g NaCl dissolved in 0.350 L of water
A) 4.70 M C6H6
B)0.235 M NaCl

You are given 12.0 g of ice at -5.00 °C. How much energy is needed to melt the ice completely to water?
q = (mass) (Δt) (Cp)
q = (moles of water) (ΔHvap)

You are given 12.0 g of ice at -5.00 °C. How much energy is needed to melt the ice completely to water?
q = (mass) (Δt) (Cp)
q = (moles of water) (ΔHvap)
q = (12.0 g) (5.0 °C) (2.06 J g¯1 °C¯1)
q = 123.6 J = 0.1236 kJ
+
q = (12.0 g) (5.0 °C) (2.06 J g¯1 °C¯1)
q = 123.6 J = 0.1236 kJ
=
4.14 kJ

For many years drinking water has been cooled in hot climates by evaporating it from the surfaces of canvas bags or porous clay pots. How many grams of water can be cooled from 35 C to 20 C by the evaporation of 60 g of water? (The heat of vaporization of water in this temperature range is 2.4 kJ/g. The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g-K.)
q = (mass) (Δt) (Cp)
q = (moles of water) (ΔHvap)

For many years drinking water has been cooled in hot climates by evaporating it from the surfaces of canvas bags or porous clay pots. How many grams of water can be cooled from 35 C to 20 C by the evaporation of 60 g of water? (The heat of vaporization of water in this temperature range is 2.4 kJ/g. The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g-K.)
q = (mass) (Δt) (Cp)
q = (moles of water) (ΔHvap)

Ethanol (C2H5OH) melts at -144 C and boils at 78 C. Its density is 0.789 g/mL. The enthalpy of fusion of ethanol is 5.02 kJ/mol. The specific heats of solid and liquid ehtanol are 0.97 J/g-K and 2.3 J/g-K, respectively.
A)How much ethanol is required to to convert 25.0 g of ethanol at 25 C to the vapor phase at 78 C?
B) How much heat is required to convert 5.00 L of ethanol at -140 C to the vapor phase at 78 C?

Ethanol (C2H5OH) melts at -144 C and boils at 78 C. Its density is 0.789 g/mL. The enthalpy of fusion of ethanol is 5.02 kJ/mol. The specific heats of solid and liquid ehtanol are 0.97 J/g-K and 2.3 J/g-K, respectively.
A)How much ethanol is required to to convert 25.0 g of ethanol at 25 C to the vapor phase at 78 C?
B) How much heat is required to convert 5.00 L of ethanol at -140 C to the vapor phase at 78 C?
A) 24.0 kJ
B) 5.57*10^3 kJ


| Team 1 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 2 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 3 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 4 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 5 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 6 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 7 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 8 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 9 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 10 |
 |
|
 |
|

What Would You Like To Risk?

| Team 1 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 2 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 3 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 4 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 5 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 6 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 7 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 8 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 9 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 10 |
 |
|
 |
|
Go To The Final Question
Final Score:

| Team 1 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 2 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 3 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 4 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 5 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 6 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 7 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 8 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 9 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 10 |
 |
|
 |
|

Edit This Game:

|
|














 What are these structures representing?
What are these structures representing?


