| Anatomy | Ultrasound | CT & MRI | General | Pandora's box |
| 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Final Question | ||||


what is the primary differential for the following:
https://radiopaedia.org/cases/75784/studies/87155?lang=gb
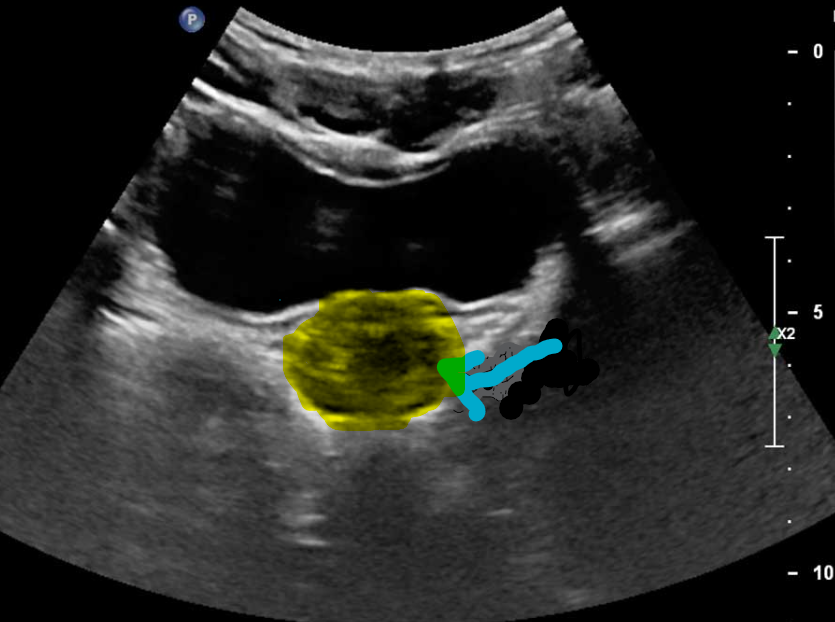
Seminoma
U/S:
-
seminomas usually appear as a homogeneous intratesticular mass of low echogenicity compared to normal testicular tissue
-
the mass is usually oval and well-defined in the absence of local invasion
-
usually confined within the tunica albuginea, rarely extending to para-testicular structures
-
-
internal blood flow is seen on colour Doppler imaging
-
cystic regions and calcifications are less common than in non-seminomatous germ cell tumours
-
larger seminomas can have a heterogeneous appearance

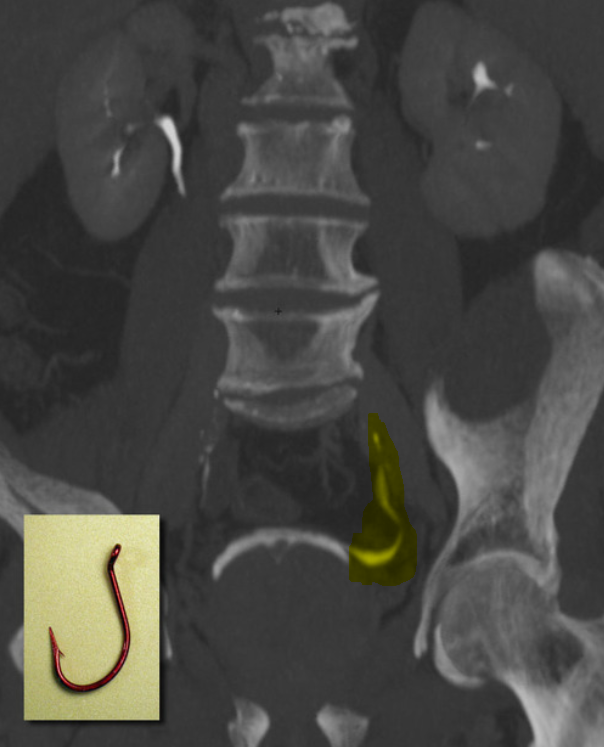
name the finding and give 2 acquired or 2 congenital etiology.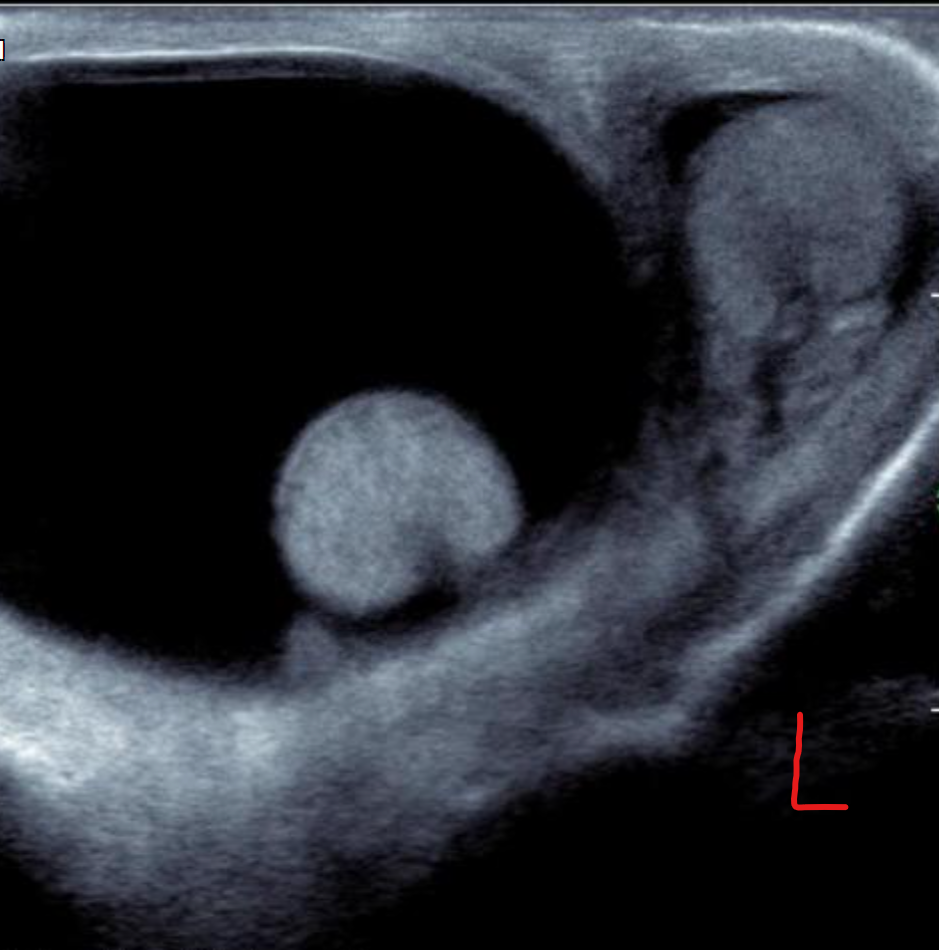
Hydrocele
Aetiology
Congenital
There are two main subtypes of congenital hydrocele:
-
communicating hydrocele
-
spermatic cord hydrocele
In the communicating type, fluid collects around a patent processus vaginalis which failed to successfully obliterate.
The spermatic cord hydrocele is further subdivided into:
-
encysted type (spermatic cord cyst): no communication with the peritoneum or tunica vaginalis
-
funicular type (funiculocele)
-
communicates with the peritoneum at the internal ring and does not surround the testis
-
more common in children and premature infants
-
Acquired
-
trauma
-
epididymitis
-
testicular torsion
-
testicular neoplasm
-
testicular infarction

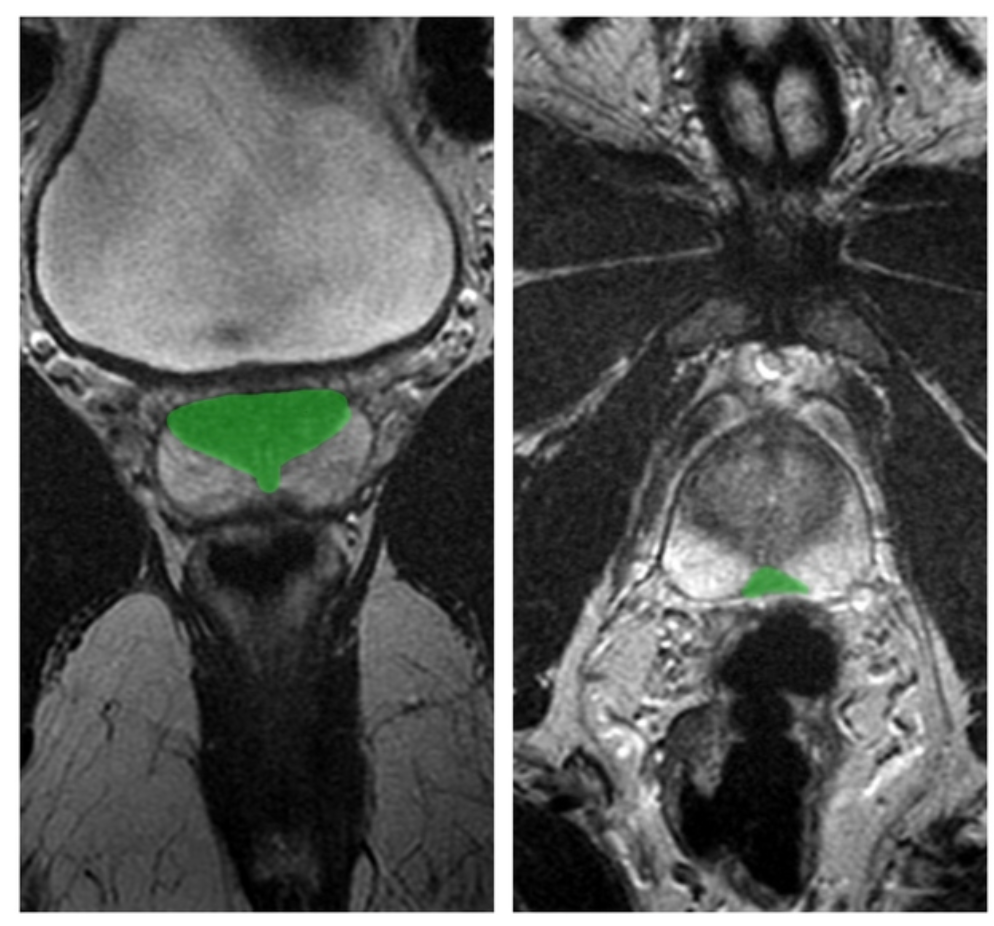
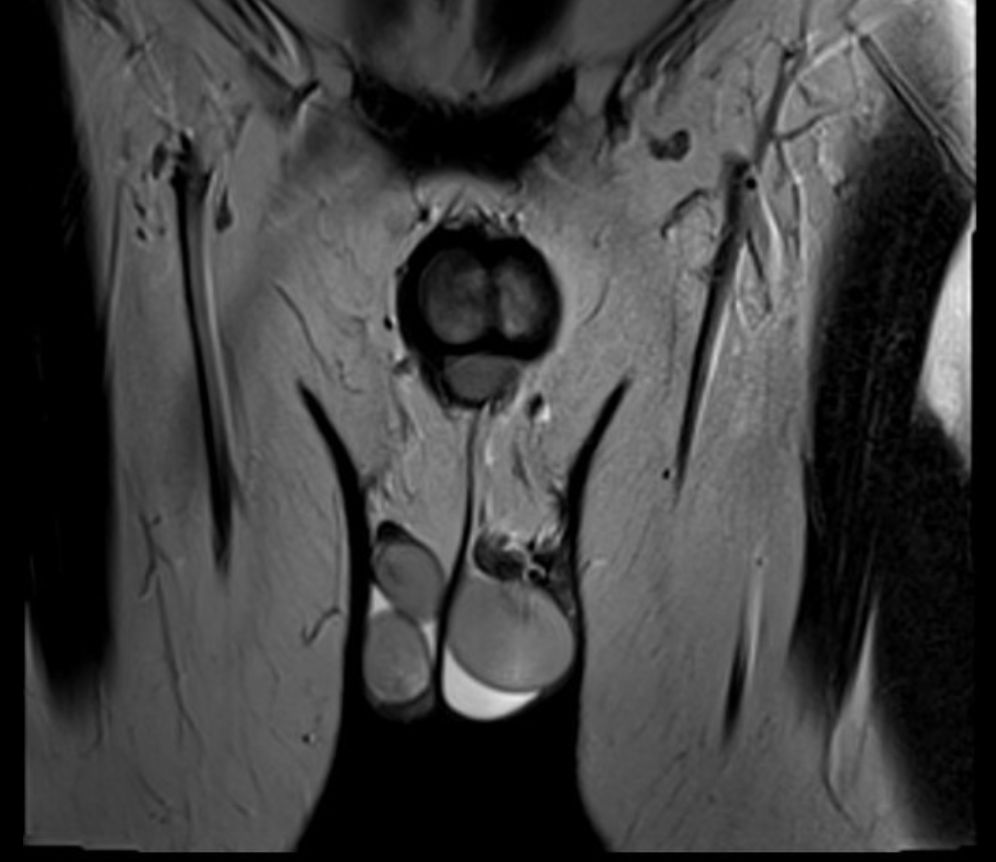
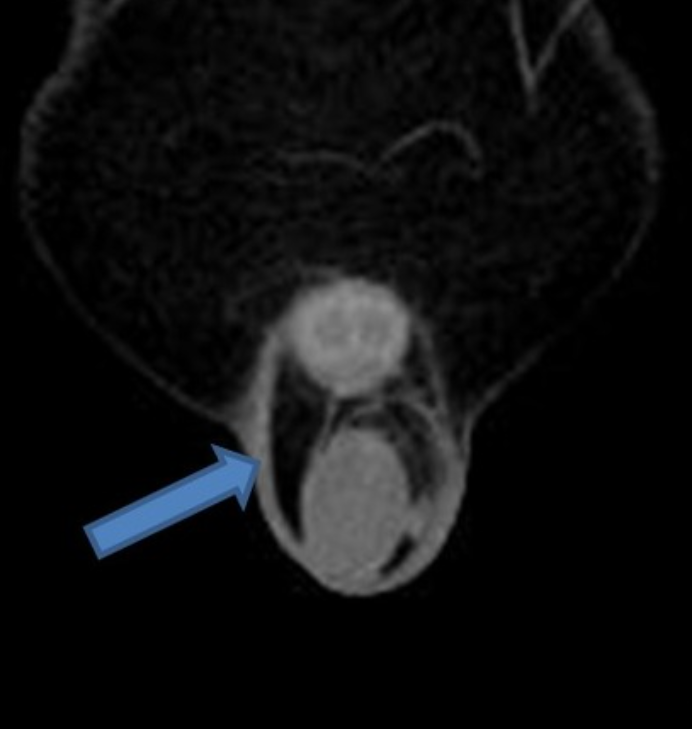
name 2 central and 2 lateral cystic lesions/cyst-like lesions of the prostate. (you can do 1/3 split)
midline cystic lesions/cyst-like lesions
- Mullerian duct cyst
- prostatic utricle cyst
- ejaculatory duct cyst (tends to be more paramedian 6)
- cystadenoma of prostate
- ductus deferens cyst
- TURP defect
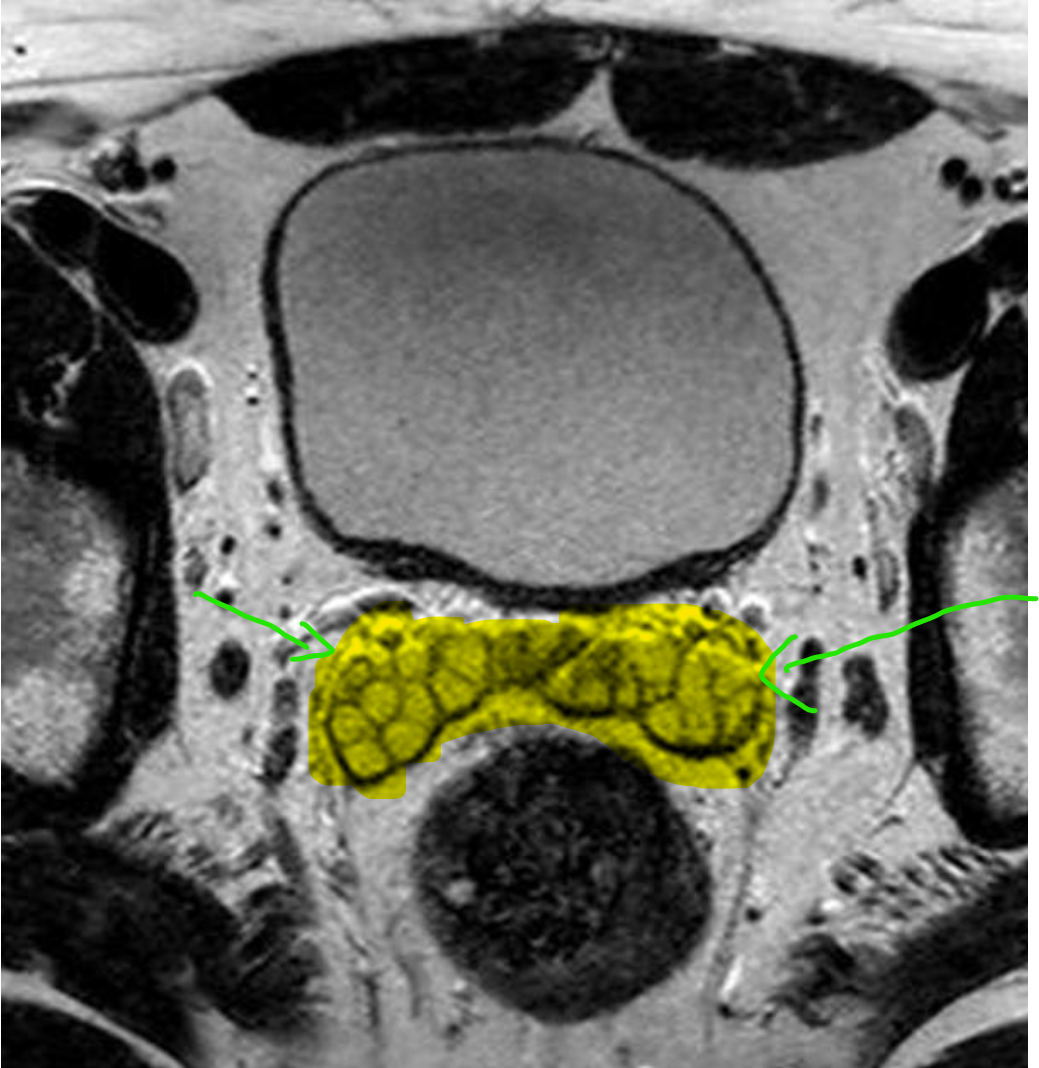
lateral cystic lesions
- cystic degeneration of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- prostatic retention cyst
- seminal vesicle cyst
- diverticular prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
- cavitatory prostatitis from chronic prostatitis
- parasitic prostatic cyst
- cystic prostatic carcinoma

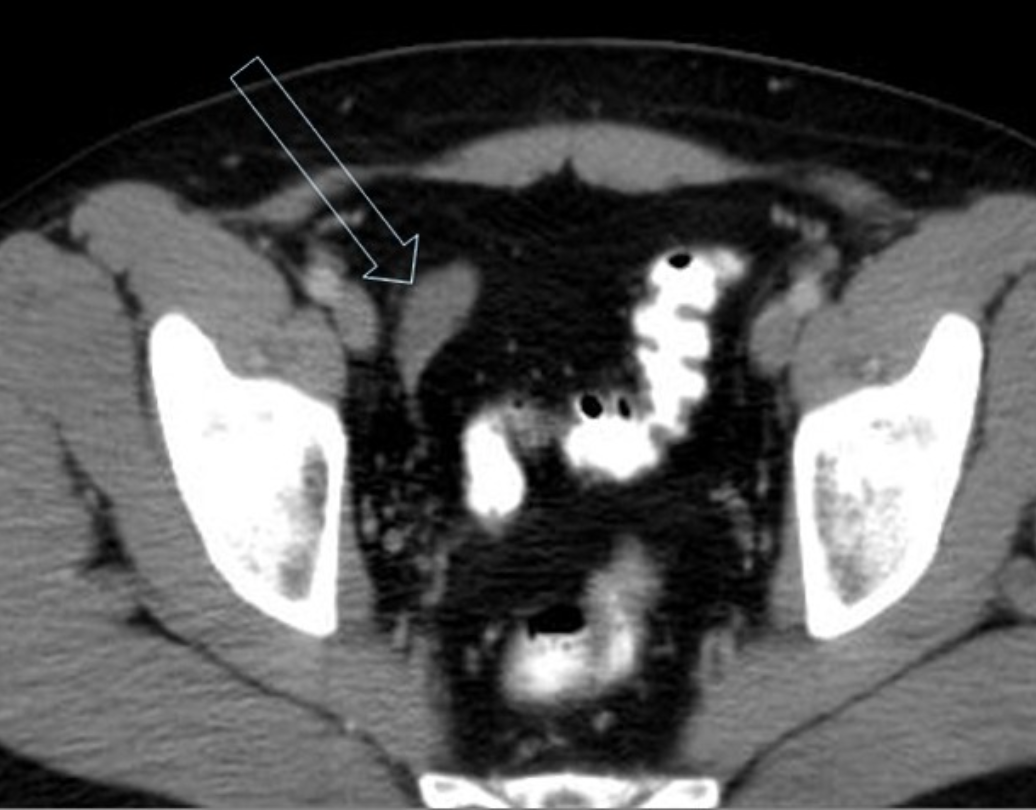
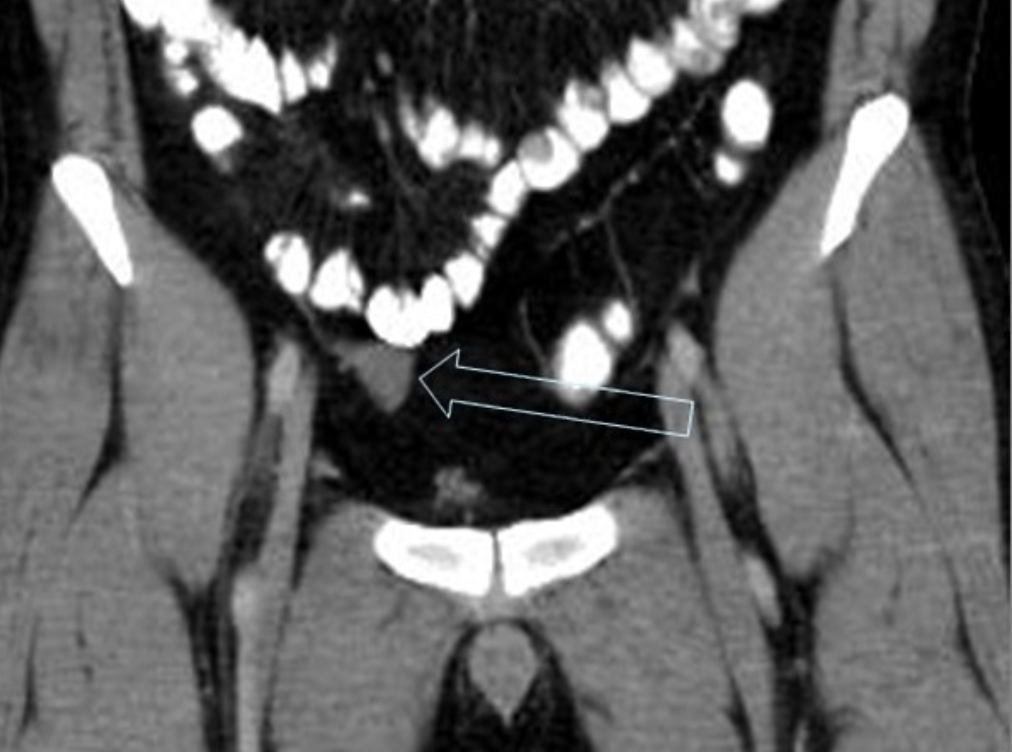
what is the difference between primary and secondary varicocele?
which testes is more commonly affected and why?
Primary varicocele
Most varicoceles are primary and result from incompetent or congenitally absent valves in the testicular vein (internal spermatic vein).
Secondary varicocele
Secondary varicoceles are much less common and result from increased pressure in the testicular vein due to compression (e.g. extrinsic mass such as retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy or renal mass, or renal vein compression in nutcracker syndrome), obstruction (e.g. renal vein thrombus), or splenorenal shunting (portal hypertension).
The left testis is affected much more commonly affected (≈85%) than the right.
This may be due to the shorter course of the right testicular vein and its oblique insertion into the IVC which creates less backpressure. In contrast, the left testicular vein has a longer course and inserts into the left renal vein at a right angle.
Bilateral varicoceles are not uncommon (≈15%).

what is the normal testes size?
get 20 extra points if you can tell newborn testes size.
Normal adult testes measure approximately 3 cm (AP) x 2-4 cm (TR) x 3-5 cm (length), with a volume of 12.5-19 mL
At birth, testes measure approximately 1.5 cm (length) x 1 cm (width), reaching ~4 mL volume at puberty

what is your primary differential for this case?
https://radiopaedia.org/cases/13513/studies/13445?lang=gb
https://radiopaedia.org/cases/59368/studies/66726?lang=gb#images

what is your primary differential for this case?
https://radiopaedia.org/cases/13513/studies/13445?lang=gb
https://radiopaedia.org/cases/59368/studies/66726?lang=gb#images
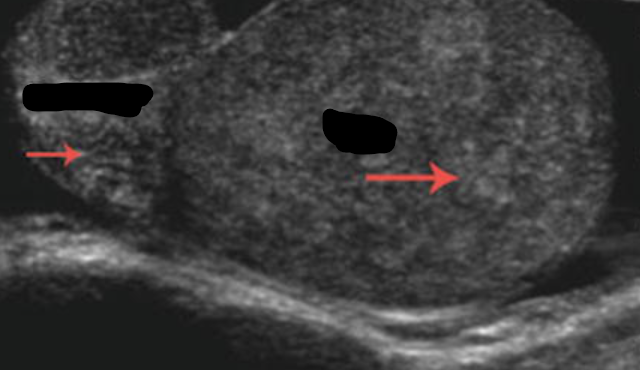
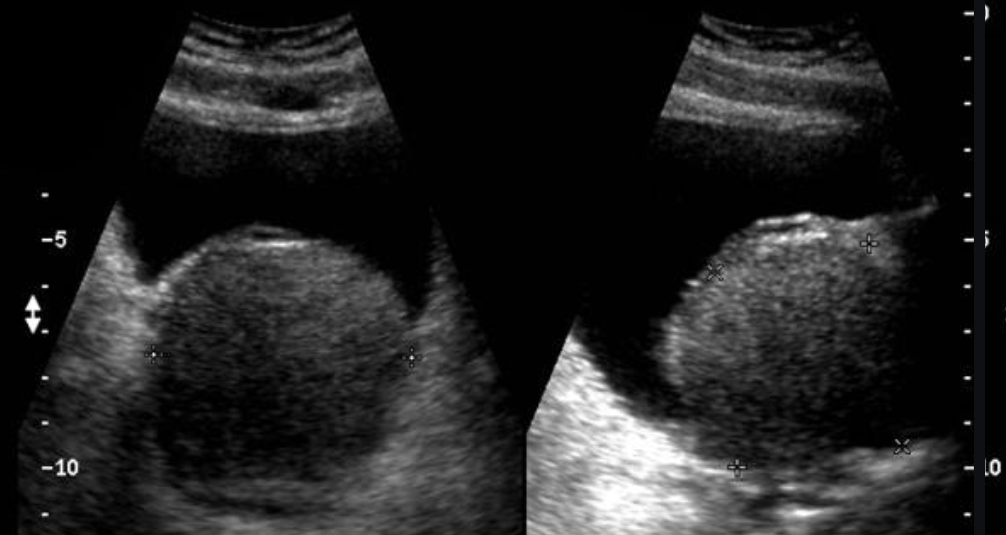
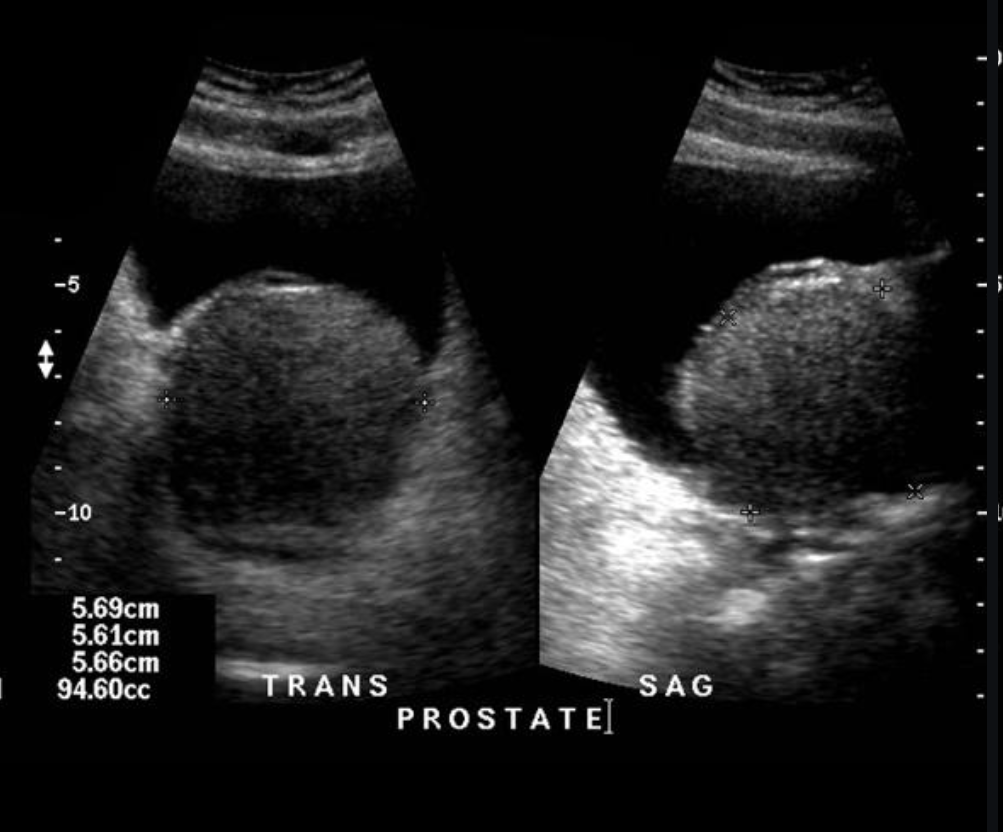
Prostatic abscess
U/S:
It usually demonstrates ill-defined hypoechoic areas within an enlarged and/or distorted prostate gland. There may be inhomogeneous echoes within these ill-defined areas.
CT:
The prostate is replaced by a large collection of peripherally enhancing, low-attenuation fluid which extends into the left ischioanal fossa. Thickening of the bladder base, likely due to reactive inflammation.

what is the difference between the 3rd and 4th grade of varicoceles on doppler?
- grade III
- no major dilatation in supine position
- dilated veins up to lower pole of testis seen only in standing position
- reflux at lower pole veins during Valsalva manoeuvre
- grade IV
- dilated veins even in supine position
- reflux during Valsalva manoeuvre

testicular cancer by decade.
fill for 3 decades. or give 4 answers.
-
1st decade: 2 answers
-
2nd decade: 1 answers
-
3rd decade: 1 answers
-
4th decade: 1 answers
-
≥7th decade: 2 answers
-
1st decade: yolk sac tumour and testicular teratoma
-
2nd decade: choriocarcinoma
-
3rd decade: embryonal cell carcinoma
-
4th decade: seminoma
-
≥7th decade: lymphoma (usually non-Hodgkin lymphoma) and spermatocytic seminoma

What Would You Like To Risk?

|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Review Game Info:

You must save this address to be able to find and share your game!