|
Macromolecule Review
What are the building blocks of carbohydrates?

What are the building blocks of carbohydrates?
sugars (or monosaccharides)

What is the most important function of carbohydrates?

What is the most important function of carbohydrates?
provide energy

Plants store energy in the form of a polysaccharide known as _____.

Plants store energy in the form of a polysaccharide known as _____.
starch

Maltose, shown here, is a ______. 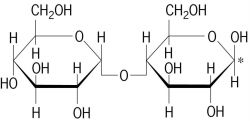

Maltose, shown here, is a ______. 
disaccharide

Cellulose is a type of carbohydrate that provides _____ in plants.

Cellulose is a type of carbohydrate that provides _____ in plants.
structural support

What is the building block of lipids?

What is the building block of lipids?
long chains of carbon and hydrogen (fatty acids)

What is the type of lipid that makes up the cell membrane?

What is the type of lipid that makes up the cell membrane?
phospholipid

These types of fats have all single bonds and occur in long, straight chains.

These types of fats have all single bonds and occur in long, straight chains.
saturated

This image shows what type of lipid? 

This image shows what type of lipid? 
unsaturated fat

This function of lipids is possible because lipids are nonpolar.

This function of lipids is possible because lipids are nonpolar.
water barrier

What is the building block of nucleic acids?

What is the building block of nucleic acids?
nucleotides

The function of nucleic acids is to store _____.

The function of nucleic acids is to store _____.
hereditary information

This example of a nucleic acid is double-stranded.

This example of a nucleic acid is double-stranded.
DNA

This example of a nucleic acid is single-stranded.

This example of a nucleic acid is single-stranded.
RNA

In what part of your cell do you find your DNA?

In what part of your cell do you find your DNA?
nucleus

What is the building block of proteins?

What is the building block of proteins?
amino acids

What is the name for a protein that helps chemical reactions happen more easily?

What is the name for a protein that helps chemical reactions happen more easily?
enzyme

What types of foods are high in proteins?

What types of foods are high in proteins?
meat, eggs, fish, nuts, etc.

Proteins are useful for transporting materials across the _____.

Proteins are useful for transporting materials across the _____.
cell membrane

Proteins help enable movement because they make up what part of our bodies?

Proteins help enable movement because they make up what part of our bodies?
muscles

Enzymes speed up reactions by _____ activation energy.

Enzymes speed up reactions by _____ activation energy.
lowering

An enzyme always acts on a specific _____.

An enzyme always acts on a specific _____.
substrate

What do you call the area of an enzyme where it binds to the molecule it is working on?

What do you call the area of an enzyme where it binds to the molecule it is working on?
active site

The _____ are released from the enzyme after the reaction has taken place.

The _____ are released from the enzyme after the reaction has taken place.
products

_____ happens if an enzyme is overheated or placed in a solution that is too acidic.

_____ happens if an enzyme is overheated or placed in a solution that is too acidic.
denaturation

All of the types of molecules we have studied are _____-based.

All of the types of molecules we have studied are _____-based.
carbon


| Team 1 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 2 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 3 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 4 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 5 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 6 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 7 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 8 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 9 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 10 |
 |
|
 |
|

What Would You Like To Risk?

| Team 1 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 2 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 3 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 4 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 5 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 6 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 7 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 8 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 9 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 10 |
 |
|
 |
|
Go To The Final Question
Final Score:

| Team 1 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 2 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 3 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 4 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 5 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 6 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 7 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 8 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 9 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Team 10 |
 |
|
 |
|

Edit This Game:

|
|












