| Anatomy | More Anatomy | Tracts | Vasculature | |
| 100 | 100 | 300 | 100 | 5 |
| 200 | 200 | 300 | 200 | 10 |
| 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 15 |
| 400 | 700 | 300 | 400 | 20 |
| 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Final Question | ||||


What is filum terminale and what does it consist of?
delicate strand of fibrous tissue, about 20 cm in length, proceeding downward from the apex of the conus medullaris. Extends to S2 level.
Consists of a pia, ependymal cells, glia and fat.

Where is C1 sensory dermatome?
Does not exist.
C1 - suboccipital nerve, which provides motor innervation to muscles at the base of the skull

What is Nucleus of Clarke?
Dorsla nucleus located at the base of dorsal horn and extends throughout thoracic spinal cord (T10-L2). Important structure for proprioception


Describe layers.
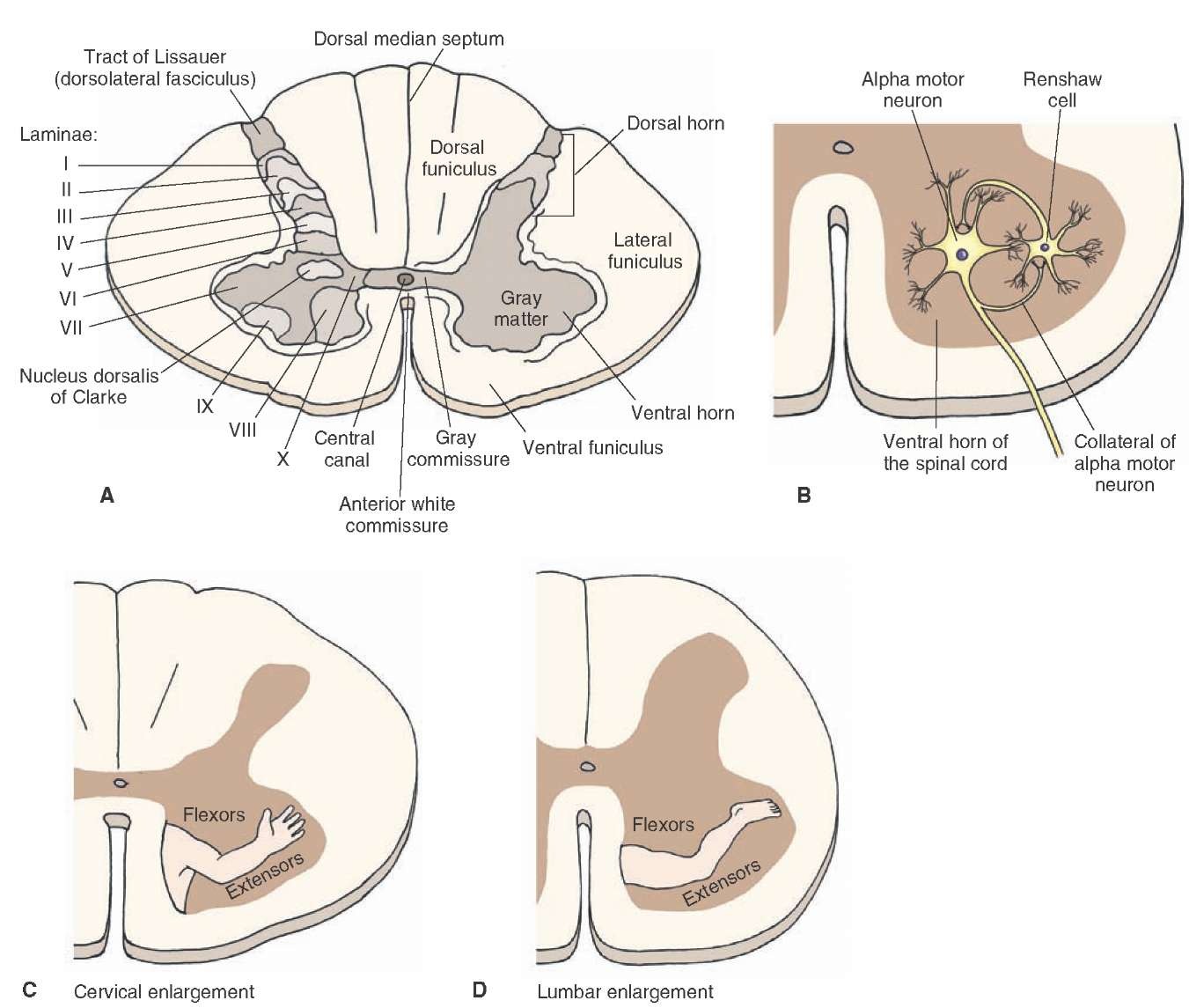
Rexed lamina I – noxious and thermal stimuli.
Rexed lamina II – responds to noxious stimuli.
Rexed lamina III – Most of the neurons in lamina III function as propriospinal/interneuron cells.
Rexed lamina IV – carry predominantly non-noxious information. respond to stimuli such as light touch.
Rexed lamina V – carry nociceptive information from visceral organs.
Rexed lamina VI – Many of the small neurons are interneurons participating in spinal reflexes
Rexed lamina VII – neurons receive information from Rexed lamina II to VI as well as visceral afferent fibers, and they serve as an intermediary relay in transmission of visceral motor neurons impulses. The dorsal nucleus of Clarke forms a prominent round oval cell column from C8 to L3. The large cells give rise to uncrossed nerve fibers of the dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT). Cells in laminae V to VII, which do not form a discrete nucleus, give rise to uncrossed fibers that form the ventral spinocerebellar tract (VSCT). Cells in the lateral horn of the cord in segments T1 and L3 give rise to preganglionic sympathetic fibers to innervate postganglionic cells located in the sympathetic ganglia outside the cord. Lateral horn neurons at segments S2 to S4 give rise to preganglionic neurons of the sacral parasympathetic fibers to innervate postganglionic cells located in peripheral ganglia.
Rexed lamina VIII – Includes an area at the base of the ventral horn, but its shape differs at various cord levels. In the cord enlargements, the lamina occupies only the medial part of the ventral horn, where descending vestibulospinal and reticulospinal fibers terminate. The neurons of lamina VIII modulate motor activity, most probably via g motor neurons which innervate the intrafusal muscle fibers.
Rexed lamina IX – Composed of several distinct groups of large a motor neurons and small γ and β motor neurons embedded within this layer. Its size and shape differ at various cord levels. In the cord enlargements the number of α motor neurons increase and they form numerous groups. The α motor neurons are large and multipolar cells and give rise to ventral root fibers to supply extrafusal skeletal muscle fibers, while the small γ motor neurons give rise to the intrafusal muscle fibers. The α motor neurons are somatotopically organized.
Rexed lamina X – Neurons in Rexed lamina X surround the central canal and occupy the commissural lateral area of the gray commissure, which also contains decussating axons.


What Would You Like To Risk?

|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Review Game Info:

You must save this address to be able to find and share your game!








![[image[21].png]](http://lh5.ggpht.com/_RIjx_Mg4ZVM/TK9xr2XqLCI/AAAAAAAACKw/UGqTzYJPnpw/s1600/image%5B21%5D.png)
![[image[50].png]](http://lh6.ggpht.com/_RIjx_Mg4ZVM/TK9yFqOQYhI/AAAAAAAACLg/yY3ZrXnjAHk/s1600/image%5B50%5D.png)
![[image[73].png]](http://lh3.ggpht.com/_RIjx_Mg4ZVM/TK9yZ1ocdyI/AAAAAAAACME/-j2fSc1ETcM/s1600/image%5B73%5D.png)
![[image[87].png]](http://lh5.ggpht.com/_RIjx_Mg4ZVM/TK9yqwgaBwI/AAAAAAAACMc/OVOt7U8co8I/s1600/image%5B87%5D.png)




