
|
SuperTeacherTools |
|

|

|
Inflammation and tubercle formation of WBC's, bacilli and fibrotic tissue in the lung. Eventually scar tissue grows around and over the tubercle and the bacilli become inactive. When there is new inflammation the scar tissue is broken through and the bacilli are re-activated.
What is pleural effusion and treatment includes thoracotomy with chest tube for drainage and antibiotics?
What is mild: Severe obstructive inflammation and edema to epiglottis with symptoms of high fever, sore throat, inspiratory stridor due to upper airway constriction, and muffled voice.
What is severe: Severe obstructive inflammation and edema to epiglottis with symptoms of inability to swallow, drooling, anxiety, pallor, tripod position (leaning forward), and severe respiratory distress.
What is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes thick mucous production as a result of a mutation of the CFTR gene. The CFTR maintains balance of salt and water on body surfaces. When deficient chloride channels is trapped in cells, the mucous covering cells becomes thick and sticky and sodium levels become elevated.
What is tuberculosis?
What is asthma?

What is the right side of the heart?
1. What is wheezing?
2. What is stridor?
3. What are retractions?
With long exhalations, patients use a puffing respiratory effort to try to blow off excess CO2.
What is CAP?
1. streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus)
2. staphylococcus aureus (from IV drug use)
What is HAP?
2. staphylococcus aureus (from central line)
What is a viral infection (parainfluenza, influenza A or RSV) with a seal-like barking cough, that usually resolves in 24-48 hours.
What is Bronchiolitis?
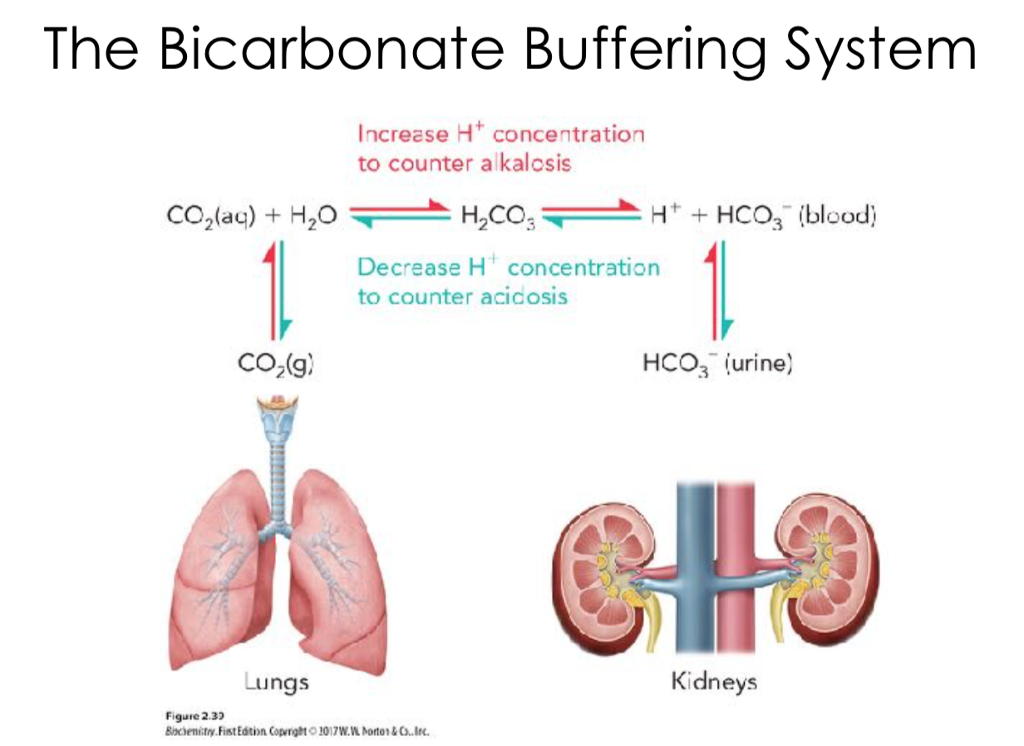
The body has chemical buffers: bicarbonate and phosphate ions. When these buffers are unable to balance the bodies ph, then the lungs assist with CO2 and the kidneys assist with HCO3. Normal ph range is (<=acidosis) 7.35-7.45(>=alkalosis)

Due to shrunken alveoli, O2 is decreased at the alveolar level causing cyanosis.

What is pulmonary hypertension?
What are mast cells?
What are Cheyne Stokes respirations?
What are increased mucous production, inflammation in bronchioles, cough, wheezing, chronic hypoxia, clubbing of fingers, and cyanosis.
Pathophysiology: hypoxia and cyanosis due to shrunk alveoli (atelectasis) causing decreased O2.
What are prolonged exhalation, barrel-shaped chest, and chronic hypercapnia?
Pathophysiology is persistent inflammation that causes bronchoconstriction, weight loss, muscle weakness and increased risk of infection. Also hyperexpansion of the chest from air trapping.
Emphysema = pink = increased CO2 due to hyperexpansion of alveoli due to loss of elasticity which causes CO2 retention.

What is low and slow!
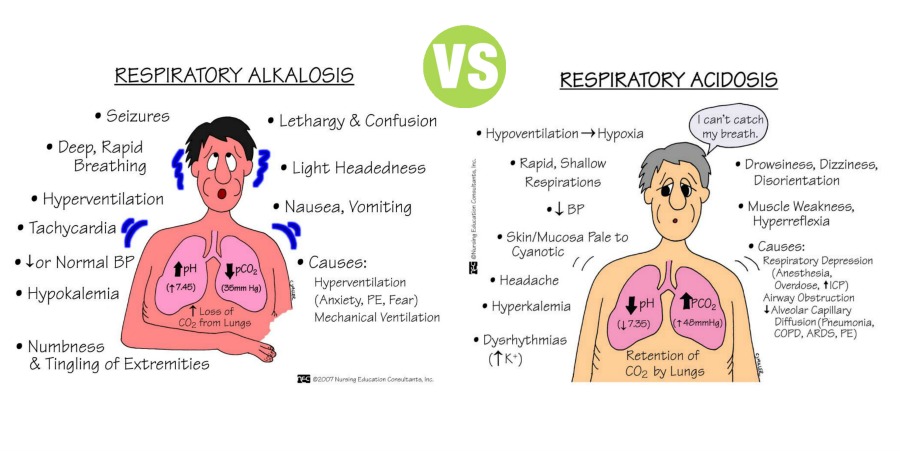
Acidosis: Hypoventilation, bronchitis, and airway constriction.
Alkalosis: Hyperventilation, asthma, anxiety
1. What is dyspnea?
2. What is orthopnea?
What are Kussmauls respirations?
List 4 symptoms and the pathophysiology of Bronchitis.
This is a disease caused by gram-positive acid-fast bacillus?
This side of the heart sends blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
Describe the process with acid/base balance.
This is a buildup of fluid in the pleural space cause by infection, heart failure, and tumors. What is the treatment for this?
What are patients with Bronchitis called "Blue Bloaters"?
List pathophysiology of mild and severe epiglottis and 3 symptoms of each.
List 4 symptoms and pathophysiology of emphysema.
This breathing alternates rapid breathing with periods of apnea and often seen with brain stem injuries.
This breathing is found in a patient with DKA and has increased respiratory rate, and long expirations.
Describe the pathophysiology of Cystic Fibrosis.
This cell stimulates the release of histamines causing airway inflammation and mucous production.
1. This sound is due to swelling in the bronchials.
2. This sound is due to upper airway constriction.
3. These are seen when a patient is in severe respiratory distress.
This are the causes of infection in CAP and HAP infections.
Describe ventilation to perfusion ratio and what can cause a mismatch.
This happens as a result of chronic hypoxia.
Name 3 causes for respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis.
Describe the pathophysiology of TB with active and inactive.
1. This term describes difficult or labored breathing.
2. This term describes dyspnea while lying flat.
This is the appropriate delivery of oxygen to patients with Chonic Bronchitis?
Why are patients with Emphysema called "Pink Puffers"?
Name the common cause of croup, classic symptom, and the length symptoms in mild cases?
This condition has edema, inflammation, constriction and mucous production in the bronchioles and lower respiratroy tract.
Symptoms of this disease include wheezing, use of accessory muscles, and retractions as a result of exposure to an allergen or activity.


| Description | Match: |
Describe ventilation to perfusion ratio and what can cause a mismatch. | The ratio of the amount of air reaching the alveoli to the amount of blood reaching the alveoli and should be equal. A mismatch can occur when there is a pulmonary embolism blocking oxygens ability to reach the alveolar level. |
This breathing is found in a patient with DKA and has increased respiratory rate, and long expirations. | What are Kussmauls respirations? |
This breathing alternates rapid breathing with periods of apnea and often seen with brain stem injuries. | What are Cheyne Stokes respirations? |
1. This term describes difficult or labored breathing. 2. This term describes dyspnea while lying flat. | 1. What is dyspnea? 2. What is orthopnea? |
1. This sound is due to swelling in the bronchials. 2. This sound is due to upper airway constriction. 3. These are seen when a patient is in severe respiratory distress. | 1. What is wheezing? 2. What is stridor? 3. What are retractions? |
Symptoms of this disease include wheezing, use of accessory muscles, and retractions as a result of exposure to an allergen or activity. | What is asthma?
|
This cell stimulates the release of histamines causing airway inflammation and mucous production. | What are mast cells? |
List 4 symptoms and pathophysiology of emphysema. | What are prolonged exhalation, barrel-shaped chest, and chronic hypercapnia?
Pathophysiology is persistent inflammation that causes bronchoconstriction, weight loss, muscle weakness and increased risk of infection. Also hyperexpansion of the chest from air trapping.
Emphysema = pink = increased CO2 due to hyperexpansion of alveoli due to loss of elasticity which causes CO2 retention. |
Why are patients with Emphysema called "Pink Puffers"? | With long exhalations, patients use a puffing respiratory effort to try to blow off excess CO2. |
Name 3 causes for respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis. | Acidosis: Hypoventilation, bronchitis, and airway constriction. Alkalosis: Hyperventilation, asthma, anxiety
|
List 4 symptoms and the pathophysiology of Bronchitis. | What are increased mucous production, inflammation in bronchioles, cough, wheezing, chronic hypoxia, clubbing of fingers, and cyanosis.
Pathophysiology: hypoxia and cyanosis due to shrunk alveoli (atelectasis) causing decreased O2. |
What are patients with Bronchitis called "Blue Bloaters"? | Due to shrunken alveoli, O2 is decreased at the alveolar level causing cyanosis.
|
This is the appropriate delivery of oxygen to patients with Chonic Bronchitis? | What is low and slow! |
This side of the heart sends blood to the lungs for oxygenation. | What is the right side of the heart? |
This happens as a result of chronic hypoxia. | What is pulmonary hypertension? |
Name the common cause of croup, classic symptom, and the length symptoms in mild cases? | What is a viral infection (parainfluenza, influenza A or RSV) with a seal-like barking cough, that usually resolves in 24-48 hours.
|
List pathophysiology of mild and severe epiglottis and 3 symptoms of each. | What is mild: Severe obstructive inflammation and edema to epiglottis with symptoms of high fever, sore throat, inspiratory stridor due to upper airway constriction, and muffled voice.
What is severe: Severe obstructive inflammation and edema to epiglottis with symptoms of inability to swallow, drooling, anxiety, pallor, tripod position (leaning forward), and severe respiratory distress. |
|
|
Describe the pathophysiology of Cystic Fibrosis. | What is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes thick mucous production as a result of a mutation of the CFTR gene. The CFTR maintains balance of salt and water on body surfaces. When deficient chloride channels is trapped in cells, the mucous covering cells becomes thick and sticky and sodium levels become elevated. |
This condition has edema, inflammation, constriction and mucous production in the bronchioles and lower respiratroy tract. | What is Bronchiolitis? |
This is a disease caused by gram-positive acid-fast bacillus? | What is tuberculosis? |
This is a buildup of fluid in the pleural space cause by infection, heart failure, and tumors. What is the treatment for this? | What is pleural effusion and treatment includes thoracotomy with chest tube for drainage and antibiotics? |
This are the causes of infection in CAP and HAP infections. | What is CAP? 1. streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) 2. staphylococcus aureus (from IV drug use) What is HAP? 1. pseudomonas aeruginosa
2. staphylococcus aureus (from central line) |
Describe the pathophysiology of TB with active and inactive. | Inflammation and tubercle formation of WBC's, bacilli and fibrotic tissue in the lung. Eventually scar tissue grows around and over the tubercle and the bacilli become inactive. When there is new inflammation the scar tissue is broken through and the bacilli are re-activated. |
Describe the process with acid/base balance. | The body has chemical buffers: bicarbonate and phosphate ions. When these buffers are unable to balance the bodies ph, then the lungs assist with CO2 and the kidneys assist with HCO3. Normal ph range is (<=acidosis) 7.35-7.45(>=alkalosis)
|